
Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 100%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 88%
-
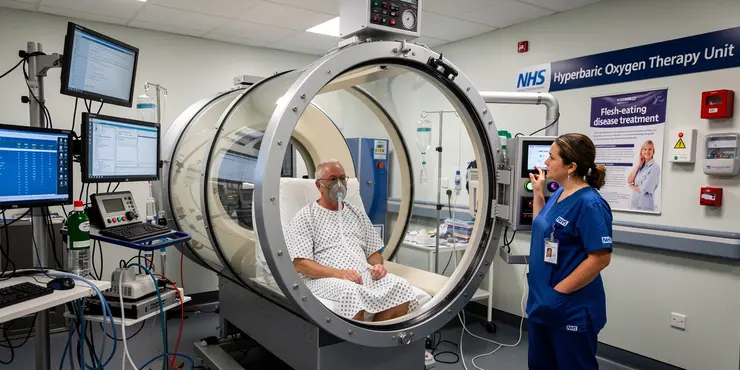
What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 87%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 84%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 83%
-
What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 83%
-
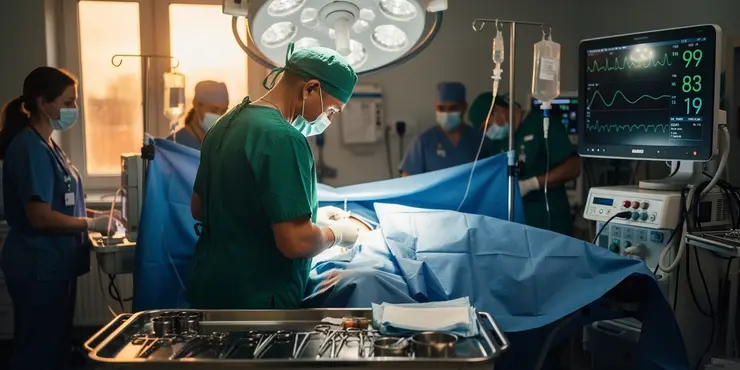
Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 83%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 80%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 79%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 78%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 76%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 75%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 75%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 73%
-
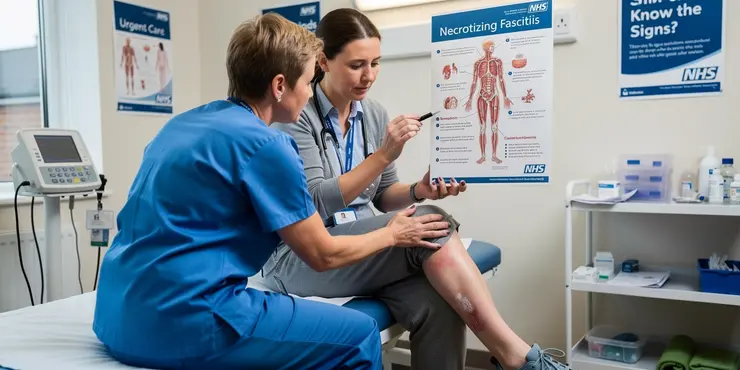
What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 73%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 72%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 72%
-
What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 70%
-
What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 66%
-

Can Lyme disease be treated?
Relevance: 53%
-

How effective are antibiotics in treating Lyme disease?
Relevance: 49%
-

How is sickle cell disease treated?
Relevance: 48%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 45%
-

What kinds of specialists are involved in treating Huntington's disease?
Relevance: 41%
-

What is Crohn’s disease and how is it treated?
Relevance: 39%
-

What is Lyme Disease?
Relevance: 39%
-
Lyme disease: What is it?
Relevance: 34%
-
What is the first sign of Lyme disease?
Relevance: 33%
-

What treatments are available for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 33%
-

What conditions is Omeprazole used to treat?
Relevance: 32%
-

What is heart valve disease?
Relevance: 32%
-

Understanding Your Sexual Health - Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Relevance: 31%
-

Is Lyme disease contagious between humans?
Relevance: 31%
-
What happens if Lyme disease is left untreated?
Relevance: 31%
-

Living with early stage kidney disease
Relevance: 31%
-

Is there a cure for motor neurone disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

Is there a cure for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 30%
-
What is Huntington's disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

Can HPV be treated?
Relevance: 30%
-

What are the complications of sickle cell disease?
Relevance: 30%
Understanding Flesh-Eating Disease
Flesh-eating disease, known medically as necrotising fasciitis, is a rare but severe bacterial infection. It rapidly destroys soft tissues and can cause shock and organ failure. Immediate medical intervention is crucial to prevent severe complications or death.
This condition is often caused by group A Streptococcus, though other bacteria may be involved. The disease can start from minor injuries or surgical wounds. Early diagnosis and treatment significantly increase the chances of recovery.
Treatment Options Available
Treatment for necrotising fasciitis typically involves a combination of antibiotics and surgery. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are administered as soon as possible to target the bacteria. These medications help slow the spread of infection, providing a crucial first line of defence.
Surgical intervention is usually necessary to remove necrotic tissue. This may involve multiple surgeries to ensure all dead tissue is excised, which helps halt the progression of the disease. This step is essential for reducing the mortality rate associated with the condition.
Importance of Early Intervention
The success of treatment largely depends on how quickly the disease is diagnosed and addressed. Early symptoms can resemble those of less severe infections, leading to delayed treatment. Common early signs include sudden severe pain, redness, and swelling at the infection site.
Seeking immediate medical attention when such symptoms appear can save lives. Healthcare professionals often rely on a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests to confirm a diagnosis swiftly.
Potential Complications
Even with prompt treatment, complications can occur. These may include extensive scarring, loss of limb function, or even amputation in severe cases. The disease can also cause rapid systemic issues, such as septic shock, which requires intensive care.
Long-term rehabilitation may be necessary for survivors to recover normal function. This could involve physical therapy or reconstructive surgeries to aid in regaining mobility and appearance.
Preventative Measures
While necrotising fasciitis can occur unpredictably, certain precautions can reduce risk. Maintaining good hygiene and promptly treating wounds are simple but effective measures. People with weakened immune systems should be particularly cautious as they are more susceptible.
Healthcare providers play a critical role in educating patients about the signs of infection, especially after surgeries or injuries. Awareness and vigilance remain key factors in preventing this aggressive disease from taking hold.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is flesh-eating disease?
Flesh-eating disease, or necrotizing fasciitis, is a rare but serious bacterial infection that destroys soft tissue, including muscle, fat, and skin.
Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Yes, flesh-eating disease can be treated, but it requires prompt and aggressive medical intervention, including antibiotics and possibly surgery.
What are the common symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis?
Symptoms include severe pain in the affected area, swelling, redness, and fever. As the disease progresses, blisters, skin discoloration, and tissue death may occur.
What causes flesh-eating disease?
It is caused by certain types of bacteria, such as group A Streptococcus, Klebsiella, Clostridium, and Escherichia coli, which invade the body's soft tissues.
How is necrotizing fasciitis diagnosed?
It is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, and laboratory analysis of blood and tissue samples.
What is the primary treatment for flesh-eating disease?
The primary treatment involves high doses of intravenous antibiotics to combat the infection and surgery to remove dead tissue.
Is surgery always necessary to treat necrotizing fasciitis?
Surgery is often necessary to remove infected and dead tissue, prevent the spread of infection, and save as much healthy tissue as possible.
Can necrotizing fasciitis lead to complications?
Yes, complications can include severe scarring, loss of limbs, and even death if not treated promptly and aggressively.
What is the prognosis for someone with flesh-eating disease?
With early diagnosis and treatment, many patients recover, but the disease can still be life-threatening and may result in permanent damage.
Who is at risk for developing necrotizing fasciitis?
Anyone can get it, but people with weakened immune systems, chronic health conditions, or those with open wounds are at higher risk.
How can necrotizing fasciitis be prevented?
Preventive measures include good hygiene, proper wound care, and avoiding exposure to contaminated water or environments if you have open wounds.
Are there specific antibiotics used to treat flesh-eating disease?
Yes, a combination of broad-spectrum antibiotics is often used, such as penicillin, clindamycin, or carbapenems, depending on the bacteria involved.
Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Recurrence is rare, but possible if contributing factors are not addressed or if any bacteria remain in the body after treatment.
How long does recovery from necrotizing fasciitis take?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the infection, treatments required, and overall health of the patient. It can take several weeks to months.
Is hospitalization required for treating necrotizing fasciitis?
Yes, due to the need for intensive treatment, including IV antibiotics and surgery, hospitalization is usually required.
Can necrotizing fasciitis spread from person to person?
Direct spread from person to person is rare. It's usually caused by bacteria entering the body through an open wound or cut.
What long-term effects might survivors of flesh-eating disease experience?
Survivors may experience chronic pain, scarring, psychological impact, or loss of function in affected areas.
What advancements in treatment are there for flesh-eating disease?
Advancements include early diagnostic techniques, advanced wound care technologies, and new surgical methods to preserve as much tissue as possible.
Is there a vaccine for necrotizing fasciitis?
There is no vaccine specifically for necrotizing fasciitis, but vaccines exist for some bacteria that can cause it, like Streptococcus pneumoniae.
How can public awareness be increased about flesh-eating disease?
Increased awareness can be achieved through educational campaigns, healthcare provider training, and public health policies aimed at prevention and early detection.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 100%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 88%
-

What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 87%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 84%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 83%
-

What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 83%
-

Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 83%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 80%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 79%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 78%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 76%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 75%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 75%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 73%
-

What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 73%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 72%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 72%
-

What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 70%
-

What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 66%
-

Can Lyme disease be treated?
Relevance: 53%
-

How effective are antibiotics in treating Lyme disease?
Relevance: 49%
-

How is sickle cell disease treated?
Relevance: 48%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 45%
-

What kinds of specialists are involved in treating Huntington's disease?
Relevance: 41%
-

What is Crohn’s disease and how is it treated?
Relevance: 39%
-

What is Lyme Disease?
Relevance: 39%
-

Lyme disease: What is it?
Relevance: 34%
-

What is the first sign of Lyme disease?
Relevance: 33%
-

What treatments are available for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 33%
-

What conditions is Omeprazole used to treat?
Relevance: 32%
-

What is heart valve disease?
Relevance: 32%
-

Understanding Your Sexual Health - Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Relevance: 31%
-

Is Lyme disease contagious between humans?
Relevance: 31%
-

What happens if Lyme disease is left untreated?
Relevance: 31%
-

Living with early stage kidney disease
Relevance: 31%
-

Is there a cure for motor neurone disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

Is there a cure for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

What is Huntington's disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

Can HPV be treated?
Relevance: 30%
-

What are the complications of sickle cell disease?
Relevance: 30%


