Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-
What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 100%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 64%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 63%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 60%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 59%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 58%
-
What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 58%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 57%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 57%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 56%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 55%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 55%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 53%
-
Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 53%
-
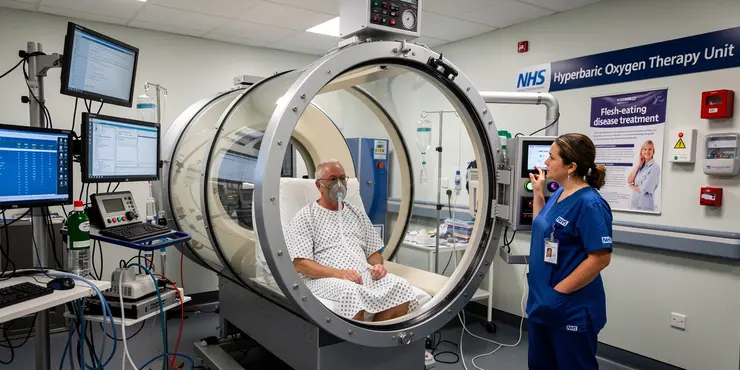
What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 53%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 52%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 50%
-
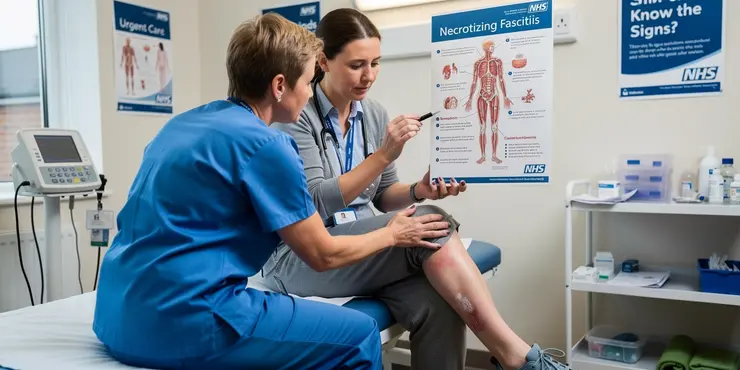
What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 50%
-

2 episodes of cellulitis and been given antibiotics but the redness doesn't seem to be improving?
Relevance: 50%
-
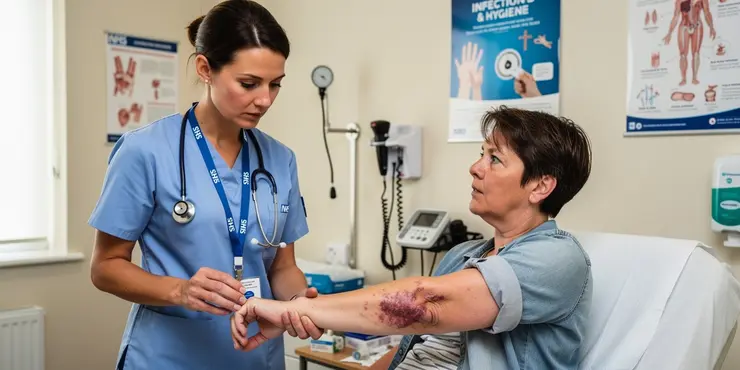
What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 48%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 34%
-
What to do about red legs
Relevance: 27%
-
Coeliac Disease: Session 1: What is Coeliac Disease?
Relevance: 21%
-

Coeliac disease
Relevance: 21%
-

What is Lyme Disease?
Relevance: 21%
-

Is Huntington's disease fatal?
Relevance: 21%
-

Causes of coeliac disease
Relevance: 21%
-

Liver disease | NHS
Relevance: 21%
-

Is Crohn's disease contagious?
Relevance: 21%
-
What is Huntington's disease?
Relevance: 21%
-

What is Mitochondrial disease?
Relevance: 21%
-
Lyme disease: What is it?
Relevance: 20%
-

Is there a cure for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 20%
-
What is Parkinson's disease?
Relevance: 20%
-

Is there a vaccine for Lyme disease?
Relevance: 20%
-

Symptoms of coeliac disease
Relevance: 20%
-

What causes Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 20%
-

What causes Huntington's disease?
Relevance: 20%
-

Can Lyme disease be treated?
Relevance: 20%
-

How is Lyme disease transmitted?
Relevance: 20%
Introduction to Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a common skin infection caused by bacteria. It typically affects the deeper layers of the skin and subcutaneous tissues. The most common bacteria responsible are Streptococcus and Staphylococcus.
This infection usually occurs when bacteria enter through a break in the skin. It often results in redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area. Left untreated, cellulitis can lead to serious complications.
Causes and Symptoms of Cellulitis
Cellulitis can occur after an injury or a skin condition that breaks the skin surface. People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to developing this condition.
Symptoms of cellulitis include a red, swollen, and hot area on the skin. Fever and chills may accompany these symptoms. If you notice these signs, it’s important to seek medical advice promptly.
Understanding Flesh-Eating Disease
Flesh-eating disease, also known as necrotising fasciitis, is a rare but severe infection. It rapidly destroys tissues under the skin and can become life-threatening.
This condition often results from various bacteria, including Group A Streptococcus. It spreads rapidly and requires immediate medical intervention.
Symptoms and Causes of Flesh-Eating Disease
Early symptoms of necrotising fasciitis may mimic less severe infections. These include redness, swelling, severe pain, and fever.
The condition progresses quickly, leading to tissue death and systemic symptoms. Risk factors include recent surgery, trauma, and underlying health issues.
Differentiating Between the Two Conditions
Though both conditions involve bacterial skin infections, their severity differs significantly. Cellulitis usually responds well to antibiotics if caught early.
Flesh-eating disease requires urgent surgical intervention and high-dose antibiotics. Unlike cellulitis, it can result in amputation or death without prompt treatment.
Treatment and Prevention
Cellulitis is typically treated with oral or intravenous antibiotics. Keeping skin moisturised and clean can help prevent breaks and infections.
For necrotising fasciitis, rapid surgical removal of affected tissue is crucial. Prevention focuses on good hygiene and wound care, especially in those with underlying health issues.
When to Seek Medical Help
Signs of cellulitis such as spreading redness and increasing pain should prompt medical consultation. Early treatment can prevent complications.
Immediate medical attention is crucial for suspected necrotising fasciitis. Symptoms like rapidly spreading infection and intense pain require emergency care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a common, potentially serious bacterial skin infection characterized by redness, swelling, warmth, and pain.
What is flesh-eating disease?
Flesh-eating disease, also known as necrotizing fasciitis, is a rare but severe bacterial infection that destroys the tissues under the skin.
What bacteria typically cause cellulitis?
Cellulitis is most commonly caused by Streptococcus and Staphylococcus bacteria.
What bacteria typically cause necrotizing fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis can be caused by various bacteria, but most commonly Group A Streptococcus, Streptococcus pyogenes.
How do the symptoms of cellulitis differ from necrotizing fasciitis?
Cellulitis symptoms include redness, warmth, swelling, and pain. Necrotizing fasciitis starts similarly but rapidly progresses with severe pain, discoloration, and tissue death.
Which condition is more life-threatening, cellulitis or necrotizing fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis is more life-threatening and requires immediate medical intervention.
Can cellulitis lead to necrotizing fasciitis?
While rare, cellulitis can progress to necrotizing fasciitis if the infection is severe and not treated promptly.
How is cellulitis diagnosed?
Cellulitis is diagnosed based on clinical examination and symptoms, sometimes supported by blood tests or cultures.
How is necrotizing fasciitis diagnosed?
Necrotizing fasciitis is diagnosed through clinical examination, imaging tests, and sometimes surgical exploration.
What are common treatments for cellulitis?
Cellulitis is typically treated with antibiotics and sometimes requires hospitalization.
What treatments are used for necrotizing fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis often requires antibiotics, surgery to remove dead tissue, and supportive care in a hospital.
What are risk factors for developing cellulitis?
Risk factors for cellulitis include skin injuries, weakened immune systems, chronic conditions like diabetes, and lymphedema.
What are the risk factors for developing necrotizing fasciitis?
Risk factors include immune suppression, chronic diseases, recent surgery, and traumatic skin injury.
How quickly does necrotizing fasciitis progress?
Necrotizing fasciitis can rapidly progress within hours, making early detection and treatment crucial.
Is cellulitis contagious?
While the bacteria causing cellulitis can spread, the condition itself is generally not considered contagious.
Is necrotizing fasciitis contagious?
Necrotizing fasciitis is not typically contagious, though the bacteria causing it can spread under rare circumstances.
What preventive measures can be taken against cellulitis?
Prevention includes proper wound care, maintaining good skin hygiene, and managing underlying health conditions.
What preventive measures can be taken against necrotizing fasciitis?
Prevention focuses on proper wound care, not delaying treatment of infections, and monitoring high-risk individuals.
Can necrotizing fasciitis occur after surgery?
Yes, necrotizing fasciitis can occur post-surgery, particularly if the incision becomes infected.
What are the long-term complications of cellulitis?
Long-term complications can include chronic swelling, recurrent infections, and in some cases, tissue damage or scarring.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 100%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 64%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 63%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 60%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 59%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 58%
-

What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 58%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 57%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 57%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 56%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 55%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 55%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 53%
-

Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 53%
-

What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 53%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 52%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 50%
-

What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 50%
-

2 episodes of cellulitis and been given antibiotics but the redness doesn't seem to be improving?
Relevance: 50%
-

What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 48%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 34%
-

What to do about red legs
Relevance: 27%
-

Coeliac Disease: Session 1: What is Coeliac Disease?
Relevance: 21%
-

Coeliac disease
Relevance: 21%
-

What is Lyme Disease?
Relevance: 21%
-

Is Huntington's disease fatal?
Relevance: 21%
-

Causes of coeliac disease
Relevance: 21%
-

Liver disease | NHS
Relevance: 21%
-

Is Crohn's disease contagious?
Relevance: 21%
-

What is Huntington's disease?
Relevance: 21%
-

What is Mitochondrial disease?
Relevance: 21%
-

Lyme disease: What is it?
Relevance: 20%
-

Is there a cure for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 20%
-
What is Parkinson's disease?
Relevance: 20%
-

Is there a vaccine for Lyme disease?
Relevance: 20%
-

Symptoms of coeliac disease
Relevance: 20%
-

What causes Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 20%
-

What causes Huntington's disease?
Relevance: 20%
-

Can Lyme disease be treated?
Relevance: 20%
-

How is Lyme disease transmitted?
Relevance: 20%


