Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-
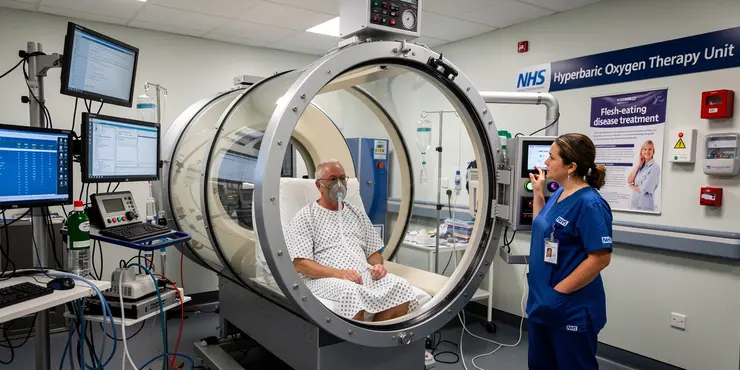
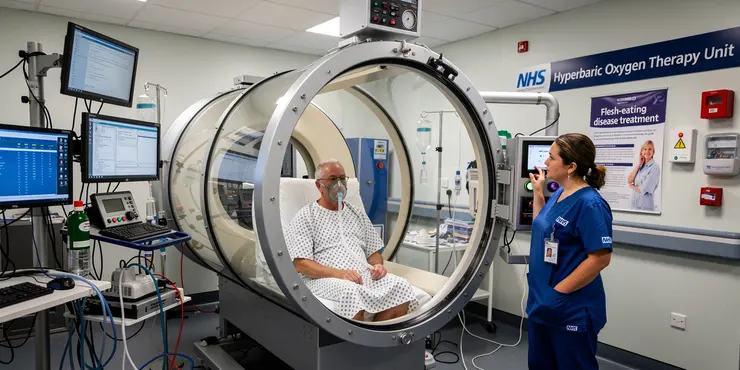
What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 100%
-
Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 51%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 51%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 39%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 38%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 37%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 37%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 37%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 36%
-
What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 36%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 35%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 35%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 34%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 33%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 32%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 31%
-
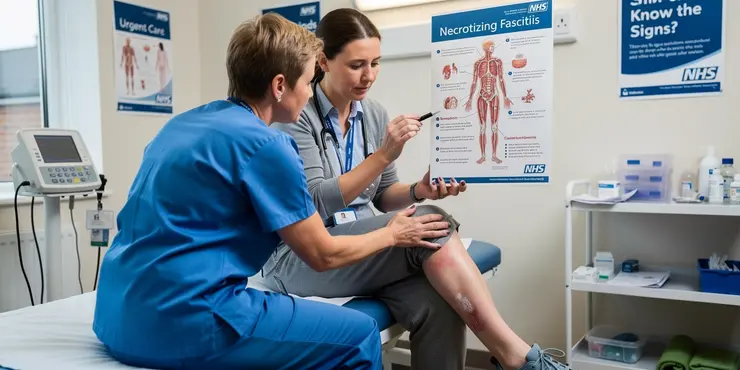
What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 31%
-
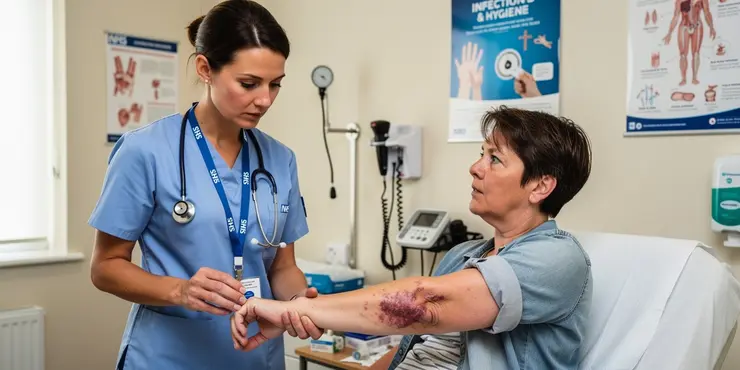
What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 30%
-
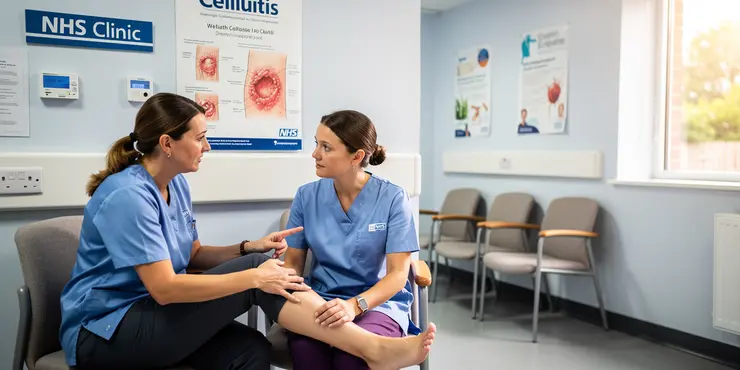
What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

How is breathing affected by motor neurone disease?
Relevance: 24%
-

How is sickle cell disease treated?
Relevance: 22%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 21%
-

Myths about COPD
Relevance: 19%
-

What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
Relevance: 19%
-

What are the complications of sickle cell disease?
Relevance: 19%
-

Is there a cure for motor neurone disease?
Relevance: 19%
-

Can Huntington's disease be cured?
Relevance: 18%
-
Hormone Therapy for prostate cancer
Relevance: 17%
-

What treatments are available for motor neurone disease?
Relevance: 17%
-

What is antiretroviral therapy (ART)?
Relevance: 17%
-

What is sickle cell disease?
Relevance: 17%
-

What is the typical progression of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 17%
-

What treatments are available for Alzheimer's disease?
Relevance: 17%
-

How does Huntington's disease affect emotions?
Relevance: 17%
-

How does hormone therapy help in treating prostate cancer?
Relevance: 17%
-

Can stress make Crohn's disease worse?
Relevance: 16%
-

Plantar Fascia Cold Therapy
Relevance: 16%
-
What is Huntington's disease?
Relevance: 16%
-

What is radiation therapy?
Relevance: 16%
-
What is Parkinson's disease?
Relevance: 16%
Understanding Flesh-Eating Disease
Flesh-eating disease, also known as necrotising fasciitis, is a rapidly progressing infection. It results in the death of soft tissue, primarily affecting the skin and muscles. The condition can become life-threatening without prompt treatment.
This disease is caused by various bacteria, with Group A Streptococcus being the most common culprit. Immediate medical intervention is crucial to prevent severe complications and fatalities. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve patient outcomes.
What is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurised chamber. This process increases the amount of oxygen in the blood. It promotes healing and fights bacterial infections effectively.
The therapy enhances white blood cell activity, aiding in the fight against infections. HBOT is used to treat various medical conditions, from decompression sickness in divers to chronic non-healing wounds.
HBOT's Role in Treating Flesh-Eating Disease
HBOT is sometimes used as an adjunctive treatment for necrotising fasciitis. It works by delivering high levels of oxygen to injured tissues, helping to reduce infection severity. This can be particularly beneficial when combined with antibiotics and surgery.
While HBOT is not a standalone cure for flesh-eating disease, it aids in slowing bacterial growth. By enhancing tissue oxygenation, it helps improve the body’s natural healing process. It also supports the efficacy of antibiotics, allowing them to penetrate deeper into infected tissues.
Benefits and Limitations
The primary benefit of HBOT in necrotising fasciitis is its ability to halt disease progression. Additionally, it can aid in faster wound healing, potentially reducing the need for extensive surgical procedures.
However, the availability of HBOT facilities can be limited in some areas. Moreover, not all patients are suitable candidates for this therapy. It is critical to assess each case individually to determine if HBOT is appropriate.
Conclusion
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a valuable tool in the treatment arsenal against flesh-eating disease. While not a cure, it complements other treatments like antibiotics and surgery. Continued research and awareness could enhance its application in managing this severe condition.
Patients with necrotising fasciitis should receive comprehensive, prompt medical care. The integration of therapies like HBOT can improve outcomes and offer hope amid a challenging diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room or chamber to promote healing and fight infection.
What is flesh-eating disease?
Flesh-eating disease, or necrotizing fasciitis, is a rare bacterial infection that spreads rapidly and destroys soft tissue.
How does hyperbaric oxygen therapy help in treating flesh-eating disease?
HBOT helps by increasing oxygen supply to the affected tissues, inhibiting bacterial growth, and enhancing the body's immune response and wound healing.
Is hyperbaric oxygen therapy a standalone treatment for necrotizing fasciitis?
No, it is usually used as an adjunct to surgery and antibiotics in comprehensive management of the disease.
How does increased oxygen pressure affect bacteria causing flesh-eating disease?
The high oxygen levels can inhibit the growth of anaerobic bacteria, which are often involved in necrotizing fasciitis.
Can HBOT improve survival rates in flesh-eating disease cases?
Studies suggest that HBOT, when combined with other treatments, may improve survival rates and reduce complications.
How often is HBOT administered in cases of necrotizing fasciitis?
The frequency and duration of HBOT sessions are tailored to the patient's condition but can be administered once or twice daily in acute cases.
What are the risks of using HBOT in treating flesh-eating disease?
Risks include ear barotrauma, sinus pressure, and, rarely, oxygen toxicity. These are generally mild and manageable.
Is HBOT effective for all types of bacteria in flesh-eating disease?
HBOT is particularly effective against anaerobic bacteria, common in necrotizing infections, but its efficacy varies with different bacterial types.
Are there any contraindications for using HBOT?
Yes, contraindications include untreated pneumothorax and certain treatments such as doxorubicin or disulfiram.
Do all hospitals offer hyperbaric oxygen therapy for necrotizing fasciitis?
Not all hospitals have HBOT facilities; it is typically available in specialized centers.
How soon should HBOT be initiated for effective results in necrotizing fasciitis?
Early intervention is crucial; initiating HBOT soon after surgical and antibiotic treatment can be beneficial.
What is the typical duration of a single HBOT session?
A single HBOT session typically lasts between 90 to 120 minutes.
Are there any long-term side effects of HBOT for flesh-eating disease patients?
Long-term side effects are rare, but some patients may experience temporary vision changes.
Is HBOT covered by insurance for treating flesh-eating disease?
Coverage varies by insurance provider, but many do cover HBOT for necrotizing fasciitis as it is considered a medically necessary treatment.
How does HBOT enhance wound healing?
HBOT promotes wound healing by increasing oxygen delivery, reducing edema, and stimulating tissue repair processes.
Is HBOT beneficial for infection control in necrotizing fasciitis?
Yes, by delivering oxygen at high pressures, HBOT can directly inhibit certain bacteria and enhance leukocyte function.
Can hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduce the need for surgical debridement?
While HBOT can support healing, it does not replace the need for surgical debridement, which remains critical in treatment.
What is the success rate of HBOT in treating necrotizing fasciitis?
Success rates can vary widely, but HBOT is generally considered a valuable adjunct therapy that can improve outcomes in many cases.
What specialists are involved in the administration of HBOT for flesh-eating disease?
HBOT is typically administered under the supervision of a specialized team including hyperbaric medicine physicians, nurses, and sometimes infectious disease experts.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 100%
-

Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 51%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 51%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 39%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 38%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 37%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 37%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 37%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 36%
-

What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 36%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 35%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 35%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 34%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 33%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 32%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 31%
-

What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 31%
-

What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

How is breathing affected by motor neurone disease?
Relevance: 24%
-

How is sickle cell disease treated?
Relevance: 22%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 21%
-

Myths about COPD
Relevance: 19%
-

What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
Relevance: 19%
-

What are the complications of sickle cell disease?
Relevance: 19%
-

Is there a cure for motor neurone disease?
Relevance: 19%
-

Can Huntington's disease be cured?
Relevance: 18%
-

Hormone Therapy for prostate cancer
Relevance: 17%
-

What treatments are available for motor neurone disease?
Relevance: 17%
-

What is antiretroviral therapy (ART)?
Relevance: 17%
-

What is sickle cell disease?
Relevance: 17%
-

What is the typical progression of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 17%
-

What treatments are available for Alzheimer's disease?
Relevance: 17%
-

How does Huntington's disease affect emotions?
Relevance: 17%
-

How does hormone therapy help in treating prostate cancer?
Relevance: 17%
-

Can stress make Crohn's disease worse?
Relevance: 16%
-

Plantar Fascia Cold Therapy
Relevance: 16%
-

What is Huntington's disease?
Relevance: 16%
-

What is radiation therapy?
Relevance: 16%
-
What is Parkinson's disease?
Relevance: 16%


