Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-
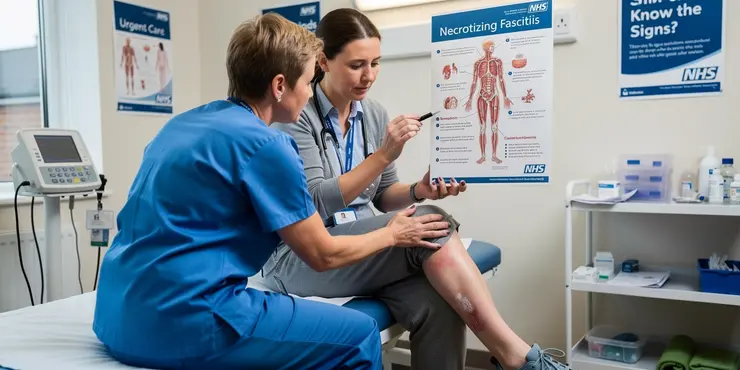
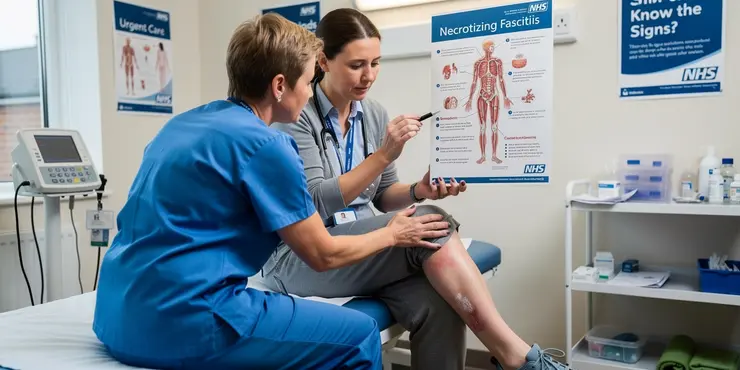
What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 100%
-

What is the mortality rate of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 77%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 67%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 64%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 64%
-

What is the mortality rate of untreated bubonic plague?
Relevance: 63%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 63%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 62%
-

What is the mortality rate of Nipah Virus infection?
Relevance: 61%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 61%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 60%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 57%
-
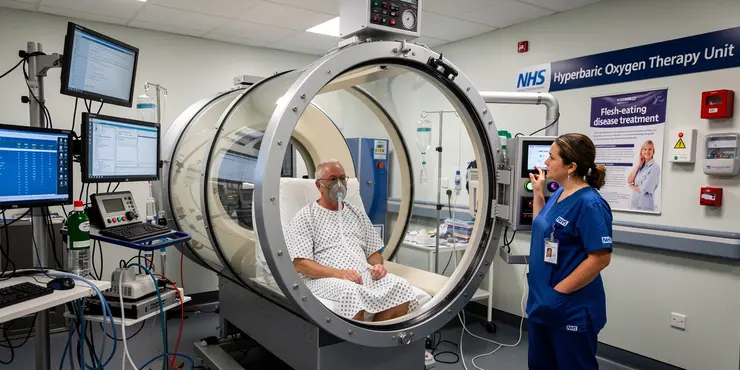
What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 55%
-
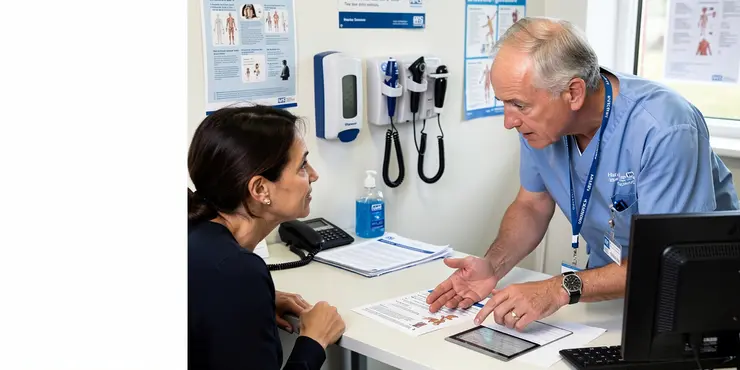
What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 55%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 54%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 54%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 53%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 52%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 51%
-
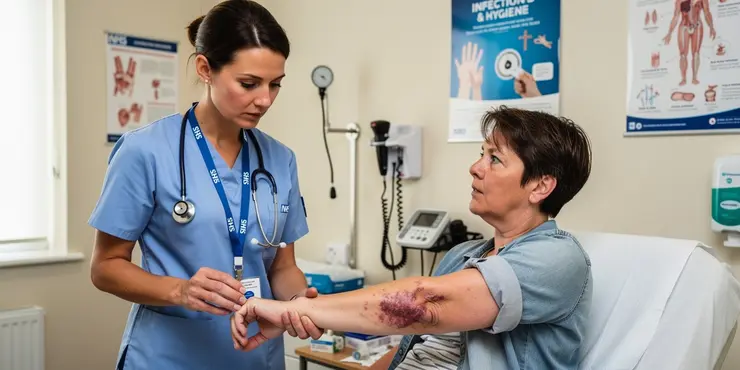
What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 46%
-
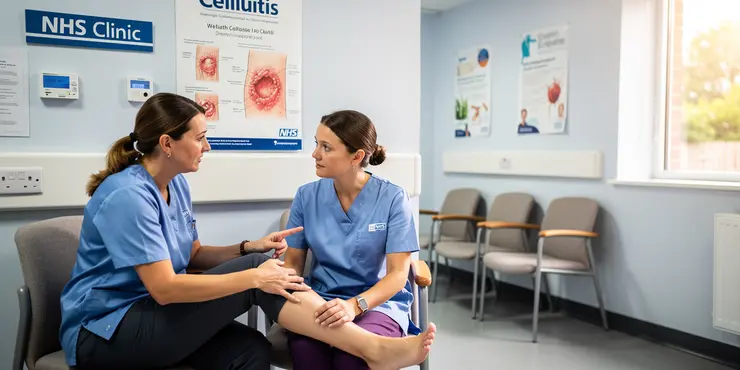
What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 46%
-
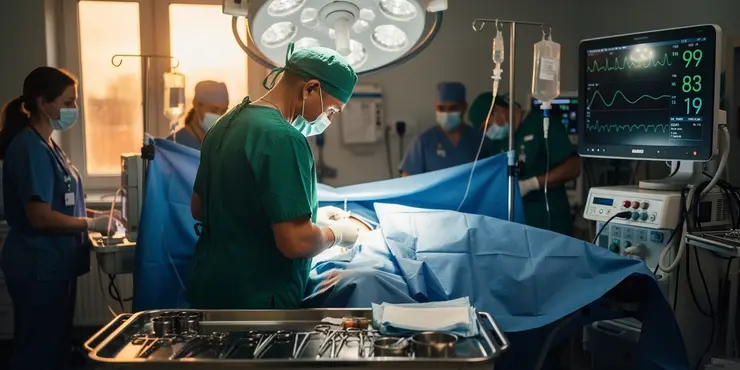
Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 44%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 33%
-
What is the Marburg Virus?
Relevance: 32%
-
Are there any populations with high seed oil usage and low disease rates?
Relevance: 32%
-

What are the symptoms of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 32%
-

How does increased screening impact bowel cancer statistics?
Relevance: 32%
-

Can Marburg virus disease recur after recovery?
Relevance: 32%
-

Why are vaccination rates declining in the UK?
Relevance: 28%
-

Can Nipah Virus cause neurological complications?
Relevance: 27%
-

What is the typical progression of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 26%
-

What is Nipah Virus?
Relevance: 24%
-

Has Marburg virus caused any major outbreaks?
Relevance: 24%
-

How do health authorities confirm a Marburg virus outbreak?
Relevance: 24%
-

How effective are antibiotics in treating Lyme disease?
Relevance: 23%
-

How does vaccination affect measles rates?
Relevance: 23%
-

Poor sense of smell in the elderly linked with higher risk of dying | NHS Behind the Headlines
Relevance: 23%
-

How is Marburg virus disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 22%
-

Why are Nipah Virus outbreaks considered a public health concern?
Relevance: 22%
-

What are the success rates of Paillon treatment?
Relevance: 22%
Understanding Flesh-Eating Disease
Flesh-eating disease, or necrotizing fasciitis, is a severe bacterial infection. It rapidly destroys muscles, skin, and tissues beneath the skin.
This condition is rare but serious. It can develop quickly and requires immediate medical attention.
Causes and Risk Factors
Flesh-eating disease is most often caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria. Other bacteria, such as Vibrio and Clostridium, can also lead to the condition.
Risk factors include cuts, surgical wounds, or weakened immune systems. Timely treatment is crucial to prevent severe outcomes.
Mortality Rate of Flesh-Eating Disease
The mortality rate for necrotizing fasciitis varies widely. Estimates indicate it ranges from 20% to 30% worldwide.
In some cases, particularly severe infections can lead to higher fatality rates. Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve survival chances.
Treatment Options
Treatment typically involves antibiotics and surgical intervention. Surgery is often needed to remove dead tissue and stop the spread of infection.
In severe cases, patients may require multiple surgeries. Intensive care support may also be necessary.
Importance of Awareness and Prevention
Public awareness is crucial in reducing mortality rates. Recognizing symptoms early can save lives.
Preventative measures include maintaining good hygiene and timely medical consultation for infected wounds. This can mitigate the risk of developing the disease.
Conclusion
Flesh-eating disease is a life-threatening condition. Understanding its risk factors and symptoms can help in reducing its mortality rate.
Prompt medical treatment and preventive measures hold the key to better outcomes. Awareness can ensure timely intervention and enhanced survival rates.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is flesh-eating disease?
Flesh-eating disease, also known as necrotizing fasciitis, is a rare but severe infection that destroys tissues under the skin.
What causes necrotizing fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis is usually caused by a bacterial infection, most commonly by Group A Streptococcus bacteria.
How does necrotizing fasciitis spread?
The bacteria that cause necrotizing fasciitis can enter the body through a break in the skin, such as a cut or surgical wound.
What are the symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis?
Early symptoms include severe pain, fever, swelling, and redness at the infection site, followed by skin changes and systemic symptoms.
What is the mortality rate for necrotizing fasciitis?
The mortality rate for necrotizing fasciitis varies but is generally reported to be around 20% to 30% even with treatment.
Why is the mortality rate for necrotizing fasciitis so high?
The mortality rate is high due to the rapid progression of the infection, potential for systemic involvement, and the need for prompt, aggressive treatment.
How can necrotizing fasciitis be diagnosed?
Diagnosis is based on clinical examination, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Suspicion of the condition requires immediate medical evaluation.
What treatments are available for necrotizing fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis requires prompt surgical intervention to remove dead tissue, along with antibiotics and supportive care.
Can necrotizing fasciitis be prevented?
Good wound care and hygiene can reduce the risk of infection, and seeking medical advice promptly for unusual symptoms can aid early diagnosis.
Who is at risk for necrotizing fasciitis?
Individuals with weakened immune systems, chronic diseases, or recent surgery are at higher risk, though it can affect healthy individuals as well.
How quickly does necrotizing fasciitis progress?
The disease can progress rapidly, often within 24 to 48 hours, making prompt treatment essential to improve outcomes.
Is necrotizing fasciitis contagious?
Necrotizing fasciitis is not usually contagious as it requires entry through a wound, but the bacteria can be spread from person to person.
Are there different types of necrotizing fasciitis?
Yes, necrotizing fasciitis can be polymicrobial or monomicrobial, depending on the bacteria causing the infection.
Can necrotizing fasciitis recur?
While rare, necrotizing fasciitis can recur or cause complications post-treatment, making follow-up care important.
What is the role of antibiotics in treating necrotizing fasciitis?
Antibiotics are crucial for treating the bacterial infection, but surgery is necessary to remove necrotic tissue.
What potential complications can arise from necrotizing fasciitis?
Complications can include sepsis, organ failure, limb amputation, and significant scarring or disfigurement.
How common is necrotizing fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis is rare, with statistics varying by region, but it is a critical medical emergency whenever it occurs.
What is the prognosis for someone with necrotizing fasciitis?
Prognosis depends on how quickly treatment is initiated and the individual’s overall health, but it can be poor without rapid intervention.
Why is rapid intervention crucial in treating necrotizing fasciitis?
Rapid intervention is crucial due to the fast progression of tissue destruction, which can lead to severe complications or death.
How can public awareness of necrotizing fasciitis be improved?
Public awareness can be improved through education about risk factors, early signs, and the importance of seeking immediate medical care.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 100%
-

What is the mortality rate of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 77%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 67%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 64%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 64%
-

What is the mortality rate of untreated bubonic plague?
Relevance: 63%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 63%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 62%
-

What is the mortality rate of Nipah Virus infection?
Relevance: 61%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 61%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 60%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 57%
-

What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 55%
-

What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 55%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 54%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 54%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 53%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 52%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 51%
-

What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 46%
-

What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 46%
-

Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 44%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 33%
-

What is the Marburg Virus?
Relevance: 32%
-
Are there any populations with high seed oil usage and low disease rates?
Relevance: 32%
-

What are the symptoms of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 32%
-

How does increased screening impact bowel cancer statistics?
Relevance: 32%
-

Can Marburg virus disease recur after recovery?
Relevance: 32%
-

Why are vaccination rates declining in the UK?
Relevance: 28%
-

Can Nipah Virus cause neurological complications?
Relevance: 27%
-

What is the typical progression of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 26%
-

What is Nipah Virus?
Relevance: 24%
-

Has Marburg virus caused any major outbreaks?
Relevance: 24%
-

How do health authorities confirm a Marburg virus outbreak?
Relevance: 24%
-

How effective are antibiotics in treating Lyme disease?
Relevance: 23%
-

How does vaccination affect measles rates?
Relevance: 23%
-

Poor sense of smell in the elderly linked with higher risk of dying | NHS Behind the Headlines
Relevance: 23%
-

How is Marburg virus disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 22%
-

Why are Nipah Virus outbreaks considered a public health concern?
Relevance: 22%
-

What are the success rates of Paillon treatment?
Relevance: 22%


