
Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 100%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 69%
-
What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 69%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 67%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 64%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 63%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 62%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 61%
-
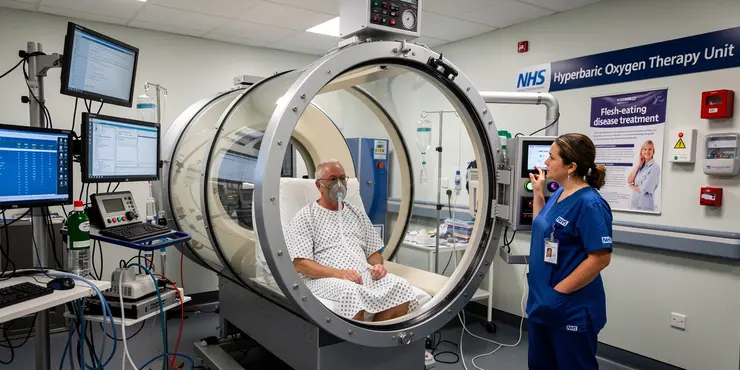
What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 60%
-
What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 60%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 59%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 59%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 59%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 58%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 57%
-
What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 55%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 54%
-
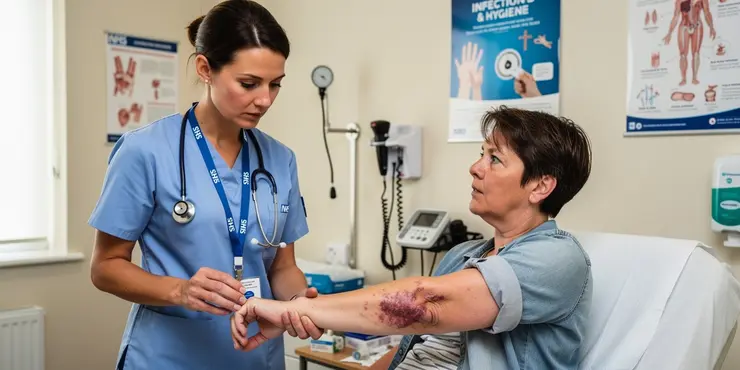
What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 53%
-
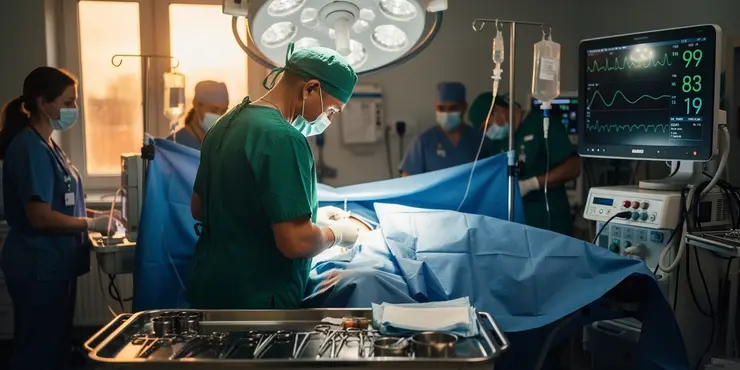
Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 49%
-

Can meningitis cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 47%
-

What are the complications of sickle cell disease?
Relevance: 43%
-

Are there any complications associated with Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 42%
-

Are there any long-term effects of gonorrhoea?
Relevance: 37%
-

What are the complications of chickenpox?
Relevance: 36%
-

Are there any long-term effects of Chikungunya infection?
Relevance: 35%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 34%
-

Can measles cause complications?
Relevance: 33%
-

Can Nipah Virus cause neurological complications?
Relevance: 33%
-

Can scabies cause complications?
Relevance: 32%
-

What are the symptoms of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 31%
-

What treatments are available for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

Are there any complications associated with shingles?
Relevance: 30%
-

Are there any complications associated with shingles?
Relevance: 30%
-

Can Lyme disease be treated?
Relevance: 30%
-

What are the potential complications of appendicitis?
Relevance: 29%
-

Is Huntington's disease fatal?
Relevance: 29%
-

Are there any long-term effects of using Ozempic?
Relevance: 29%
-

What is the typical progression of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 28%
-

Is it safe to take statins long-term?
Relevance: 28%
-

Introduction to Sickle cell disease
Relevance: 28%
Understanding Flesh-Eating Disease
Flesh-eating disease, typically known as necrotising fasciitis, is a rare but severe bacterial infection. It spreads rapidly in the body, affecting the skin, fat, and muscle layers. Timely medical intervention is crucial to control its progression.
This infection is most often caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria, among others. Early symptoms may include severe pain, swelling, and redness, quickly escalating to more serious conditions.
Immediate Treatment Is Vital
Rapid medical treatment is essential to combat necrotising fasciitis. This often involves antibiotics administered intravenously and sometimes surgical removal of the infected tissue.
Surgery helps prevent the spread of the infection by removing damaged tissue. However, aggressive treatment can leave lasting effects on the individual’s body.
Potential Long-Term Physical Complications
Survivors of flesh-eating disease may experience significant long-term complications. These often include scarring and disfigurement due to surgical interventions.
In severe cases, it may be necessary to amputate limbs to stop the infection, leading to permanent physical disability. Such drastic measures highlight the destructive nature of the bacteria.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
The aftermath of necrotising fasciitis isn't just physical. Many survivors face emotional and psychological challenges, coping with body image changes and trauma from the experience.
It's not uncommon for patients to suffer from anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress. Psychological support and counselling can be valuable in recovery.
Rehabilitation and Ongoing Care
Recovering from flesh-eating disease is often a prolonged process requiring comprehensive rehabilitation. Physical therapy is frequently needed to regain strength and mobility.
Ongoing medical care might also involve skin graft surgeries and other reconstructive procedures. Regular follow-up visits with healthcare providers ensure continued recovery and monitoring of any complications.
Preventive Measures and Awareness
Raising awareness about necrotising fasciitis can help with early detection and treatment. Keeping wounds clean and monitoring any unusual symptoms is vital.
Access to prompt medical care can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications. Staying informed about the disease equips individuals to act fast in critical situations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is flesh-eating disease?
Flesh-eating disease, also known as necrotizing fasciitis, is a severe bacterial infection that destroys muscles, skin, and underlying tissue.
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Yes, flesh-eating disease can cause long-term complications including scarring, limb loss, and functional impairments.
What types of bacteria cause flesh-eating disease?
Flesh-eating disease is often caused by Group A Streptococcus, but other bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus can also be responsible.
How is flesh-eating disease treated?
Treatment typically includes antibiotics, surgical removal of dead tissue, and supportive care. Early treatment is crucial.
What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Symptoms include severe pain, redness, swelling, blisters, fever, and fatigue. It can progress rapidly.
What are the potential long-term physical complications of flesh-eating disease?
Potential long-term physical complications include scarring, amputations, and chronic pain.
Can flesh-eating disease lead to psychological complications?
Yes, survivors may suffer from psychological issues such as PTSD, anxiety, and depression due to the traumatic nature of the disease and its treatments.
Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Preventative measures include proper wound care, good hygiene, and monitoring wounds for signs of infection.
What kind of functional impairments might someone experience after recovering from flesh-eating disease?
Functional impairments could include difficulties with movement, reduced strength, and decreased range of motion, especially if limbs were affected.
How does limb loss occur in flesh-eating disease?
Limb loss can occur if the infection is severe and tissue damage is extensive, necessitating amputation to prevent further spread.
Can reconstructive surgery help with long-term complications of flesh-eating disease?
Yes, reconstructive surgery can help improve function and appearance, although it may not fully restore the affected areas.
Is rehabilitation necessary after recovering from flesh-eating disease?
Rehabilitation is often necessary to help patients recover strength, mobility, and function, and to manage pain or prosthetic use after amputations.
What role does early diagnosis play in preventing complications from flesh-eating disease?
Early diagnosis and rapid treatment are critical to minimize tissue damage and reduce the risk of severe complications and death.
Can flesh-eating disease recur after successful treatment?
Recurrence is rare, but possible, especially if the underlying conditions or risk factors are present.
What populations are most at risk for developing flesh-eating disease?
People with compromised immune systems, diabetes, chronic diseases, and those with recent wounds are at higher risk.
What is the survival rate for individuals with flesh-eating disease?
Survival rates can vary, but with prompt treatment, many individuals survive. However, the disease can be fatal without swift medical intervention.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent long-term complications of flesh-eating disease?
Yes, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support recovery and reduce the risk of complications. This includes balanced nutrition, physical activity, and compliance with rehabilitation.
How is the severity of flesh-eating disease assessed?
Severity is assessed through clinical examination, imaging studies, and sometimes surgical exploration to determine the extent of tissue damage.
Are there support groups available for survivors of flesh-eating disease?
Yes, support groups can provide survivors and their families with emotional support, resources, and coping strategies.
What are some common myths about flesh-eating disease?
Common myths include the belief that it is highly contagious or always fatal. It requires direct contact with open wounds to spread, and with timely treatment, many survive.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 100%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 69%
-

What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 69%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 67%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 64%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 63%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 62%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 61%
-

What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 60%
-

What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 60%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 59%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 59%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 59%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 58%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 57%
-

What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 55%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 54%
-

What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 53%
-

Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 49%
-

Can meningitis cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 47%
-

What are the complications of sickle cell disease?
Relevance: 43%
-

Are there any complications associated with Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 42%
-

Are there any long-term effects of gonorrhoea?
Relevance: 37%
-

What are the complications of chickenpox?
Relevance: 36%
-

Are there any long-term effects of Chikungunya infection?
Relevance: 35%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 34%
-

Can measles cause complications?
Relevance: 33%
-

Can Nipah Virus cause neurological complications?
Relevance: 33%
-

Can scabies cause complications?
Relevance: 32%
-

What are the symptoms of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 31%
-

What treatments are available for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

Are there any complications associated with shingles?
Relevance: 30%
-

Are there any complications associated with shingles?
Relevance: 30%
-

Can Lyme disease be treated?
Relevance: 30%
-

What are the potential complications of appendicitis?
Relevance: 29%
-

Is Huntington's disease fatal?
Relevance: 29%
-

Are there any long-term effects of using Ozempic?
Relevance: 29%
-

What is the typical progression of Marburg virus disease?
Relevance: 28%
-

Is it safe to take statins long-term?
Relevance: 28%
-

Introduction to Sickle cell disease
Relevance: 28%


