
Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 100%
-
What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 72%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 69%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 67%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 66%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 65%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 64%
-
What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 64%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 64%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 63%
-
What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 63%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 63%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 62%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 61%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 61%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 59%
-
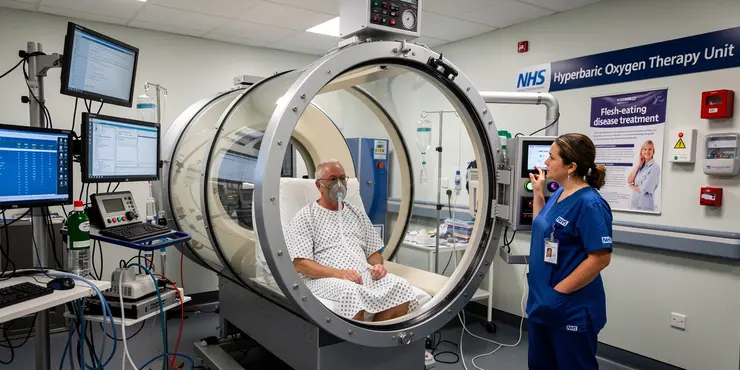
What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 58%
-

Is Crohn's disease contagious?
Relevance: 56%
-
What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 53%
-
Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 52%
-

Is Lyme disease contagious between humans?
Relevance: 48%
-

Is chickenpox contagious?
Relevance: 45%
-
Is eczema contagious?
Relevance: 45%
-

How contagious is measles?
Relevance: 43%
-
Is meningitis contagious?
Relevance: 39%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 38%
-
Is shingles contagious?
Relevance: 37%
-

Is impetigo contagious?
Relevance: 36%
-

How long is a person with measles contagious?
Relevance: 36%
-

Is the Nimbus variant more contagious?
Relevance: 36%
-

Is shingles contagious?
Relevance: 35%
-

Is the bubonic plague contagious between humans?
Relevance: 34%
-
Are nits contagious?
Relevance: 34%
-

Is the Super Flu contagious?
Relevance: 34%
-

Are cold sores contagious?
Relevance: 34%
-

Is scabies contagious?
Relevance: 33%
-

Are E. coli infections contagious?
Relevance: 31%
-
Is nettle rash contagious?
Relevance: 31%
-

Is chronic fatigue syndrome contagious?
Relevance: 31%
-

What is Lyme Disease?
Relevance: 30%
Understanding Flesh-Eating Disease
Flesh-eating disease, also known as necrotising fasciitis, is a rare but serious medical condition.
It is commonly caused by a fast-spreading bacterial infection, leading to the destruction of tissues.
Immediate medical treatment is essential to prevent severe complications or even death.
Causes of Necrotising Fasciitis
The disease is primarily caused by bacteria such as Group A Streptococcus.
Other bacteria, including certain strains of staphylococcus, can also be responsible.
Infection often occurs when bacteria enter the body through a skin break.
Is the Disease Contagious?
Flesh-eating disease itself is not considered contagious.
This means it generally does not spread from person to person.
The bacteria that cause the infection can be present without causing necrotising fasciitis.
How Transmission Occurs
The bacteria are commonly found in the environment and on people's skin.
Transmission can happen through cuts, abrasions, or surgical wounds.
Proper wound care and hygiene significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Risk Factors
People with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of developing the disease.
Chronic illnesses like diabetes also increase susceptibility to infection.
Maintaining good health and prompt wound care can minimise risks.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing skin injuries and cleaning wounds promptly are crucial.
Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment often involve antibiotics and surgery.
Seeking immediate medical attention for suspicious symptoms can save lives.
Conclusion
While necrotising fasciitis is severe, it is not easily spread between individuals.
Understanding the signs and maintaining good hygiene are key protective measures.
Awareness and prompt action are essential to managing and preventing this disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is flesh-eating disease?
Flesh-eating disease, also known as necrotizing fasciitis, is a serious bacterial infection that destroys skin, fat, and tissue covering the muscles.
Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Flesh-eating disease is not highly contagious. It typically spreads through direct contact with the bacteria, which can enter the body through open cuts or wounds.
What causes flesh-eating disease?
Necrotizing fasciitis is caused by several types of bacteria, most commonly Group A Streptococcus, but also other bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium.
How does flesh-eating bacteria spread?
It spreads through direct contact with an infected person's skin wounds or mucous membranes, but usually under conditions of weakened skin barrier or immune system.
Who is at risk for developing flesh-eating disease?
People with compromised immune systems, chronic health conditions, and open cuts or surgical wounds are at higher risk.
What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Symptoms may include severe pain near the wound site, fever, swelling, and redness that spreads quickly, leading to skin dying.
How is flesh-eating disease treated?
Treatment typically involves immediate surgery to remove infected and dead tissue, along with high-dose intravenous antibiotics.
Can flesh-eating disease be prevented?
Preventing the disease involves proper wound care, maintaining good hygiene, and avoiding exposure to contaminated water or contact with people showing symptoms.
Is it safe to be around someone with flesh-eating disease?
Yes, casual contact does not typically spread the infection, but avoid contact with their wounds or bandages.
Can flesh-eating disease reoccur?
Recurrence is rare but possible if underlying conditions are not addressed or if reinfection occurs.
What areas of the body does flesh-eating disease affect?
It can occur anywhere on the body but more commonly affects the arms, legs, and abdominal wall.
How fast does flesh-eating disease progress?
The disease can progress very rapidly, with symptoms worsening in hours to days.
What should I do if I suspect I have flesh-eating disease?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain, swelling, or fever and suspect an infection.
Are there long-term effects after surviving flesh-eating disease?
Yes, survivors may have significant scarring, disfigurement, or require reconstructive surgeries.
Do antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
No, antibiotics alone are not enough; surgery is also needed to remove dead tissue.
What are the survival rates for flesh-eating disease?
Survival rates vary but can be up to 80% with prompt treatment, though the disease can be fatal if not quickly addressed.
What medical specialists treat flesh-eating disease?
A multidisciplinary team including surgeons, infectious disease specialists, and critical care doctors typically manage treatment.
Can healthy people get flesh-eating disease?
Yes, though it’s rarer, healthy individuals can contract it if they sustain deep cuts or wounds.
What diagnostic tests identify flesh-eating disease?
Doctors may use blood tests, imaging studies (like MRI or CT scan), and surgical exploration to diagnose the condition.
How common is flesh-eating disease?
It is rare, with estimated cases ranging from 600 to 1,200 annually in the United States.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 100%
-

What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 72%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 69%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 67%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 66%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 65%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 64%
-

What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 64%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 64%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 63%
-

What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 63%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 63%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 62%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 61%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 61%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 59%
-

What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 58%
-

Is Crohn's disease contagious?
Relevance: 56%
-

What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 53%
-

Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 52%
-

Is Lyme disease contagious between humans?
Relevance: 48%
-

Is chickenpox contagious?
Relevance: 45%
-

Is eczema contagious?
Relevance: 45%
-

How contagious is measles?
Relevance: 43%
-
Is meningitis contagious?
Relevance: 39%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 38%
-

Is shingles contagious?
Relevance: 37%
-

Is impetigo contagious?
Relevance: 36%
-

How long is a person with measles contagious?
Relevance: 36%
-

Is the Nimbus variant more contagious?
Relevance: 36%
-

Is shingles contagious?
Relevance: 35%
-

Is the bubonic plague contagious between humans?
Relevance: 34%
-

Are nits contagious?
Relevance: 34%
-

Is the Super Flu contagious?
Relevance: 34%
-

Are cold sores contagious?
Relevance: 34%
-

Is scabies contagious?
Relevance: 33%
-

Are E. coli infections contagious?
Relevance: 31%
-

Is nettle rash contagious?
Relevance: 31%
-

Is chronic fatigue syndrome contagious?
Relevance: 31%
-

What is Lyme Disease?
Relevance: 30%


