
Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 100%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 76%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 73%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 73%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 72%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 67%
-
What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 66%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 66%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 65%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 65%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 65%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 65%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 64%
-
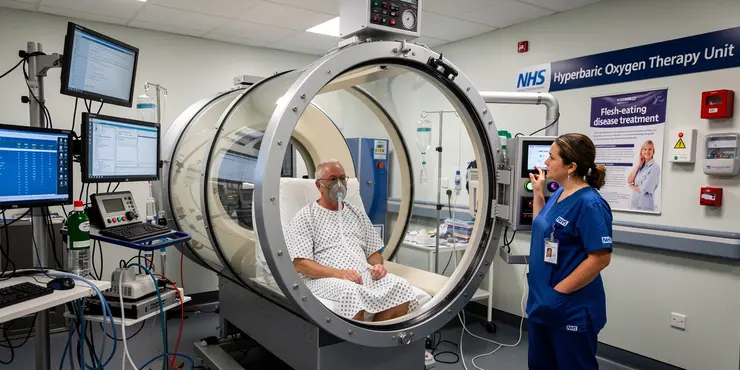
What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 63%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 62%
-
What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 62%
-
What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 60%
-
Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 58%
-
What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 55%
-

Can testicular cancer recur after treatment?
Relevance: 44%
-

Can Marburg virus disease recur after recovery?
Relevance: 44%
-

Can prostate cancer recur after treatment?
Relevance: 43%
-
Can hypotony recur after treatment?
Relevance: 42%
-

Evidence-Based Interventions: tonsillectomy for recurrent tonsillitis surgery
Relevance: 42%
-

Can BPH recur after treatment?
Relevance: 42%
-
Can postnatal depression recur after treatment?
Relevance: 41%
-

Can Carpal Tunnel Syndrome recur after treatment?
Relevance: 41%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 39%
-

How effective are antibiotics in treating Lyme disease?
Relevance: 37%
-

What treatments are available for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 36%
-

What treatments are available for Alzheimer's disease?
Relevance: 35%
-

What treatments are available for motor neurone disease?
Relevance: 34%
-

Can Lyme disease be treated?
Relevance: 33%
-

Chronic kidney disease: What are the treatments?
Relevance: 32%
-
Can I get impetigo more than once?
Relevance: 30%
-

How does smoking affect Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

What role do tumor markers play in testicular cancer?
Relevance: 30%
-

Can you get Lyme disease more than once?
Relevance: 30%
-

Is surgery necessary for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 29%
-

Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment Offers Hope for Prostate Cancer Patients
Relevance: 28%
Understanding Flesh-Eating Disease
Flesh-eating disease, also called necrotizing fasciitis, is a severe bacterial infection. It rapidly destroys the body's soft tissue, causing devastating effects.
This condition requires urgent medical attention. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and often surgery to remove dead tissue.
Causes and Risk Factors
Necrotizing fasciitis is often caused by Group A Streptococcus bacteria. Other bacteria can also cause the disease, including Vibrio vulnificus.
Certain factors increase the risk of developing this infection. These include having compromised immunity, wounds, or chronic illnesses.
Possibility of Recurrence
After treatment, the risk of recurrence is relatively low but not impossible. Recurrence can occur if the initial infection was not completely eradicated.
Re-exposure to the bacteria in vulnerable individuals can lead to another infection. Proper wound care and hygiene are crucial in prevention.
Prevention and Care
To prevent recurrence, it is essential to follow medical advice diligently. This includes completing prescribed antibiotics even if symptoms improve.
Practicing good hygiene and taking care of skin wounds can help reduce risk. Individuals with weakened immune systems should exercise extra caution.
Importance of Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals is important after treatment. Monitoring for any signs of recurrence ensures timely intervention.
If redness, swelling, or unexpected pain occurs post-treatment, seek medical advice promptly. Quick response can prevent serious complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is flesh-eating disease?
Flesh-eating disease, also known as necrotizing fasciitis, is a rare but serious bacterial infection that can destroy the skin, fat, and tissue covering the muscles.
Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Yes, flesh-eating disease can recur after treatment, although it is relatively rare. Recurrence might occur if the underlying cause is not addressed, or if a new infection occurs.
What are the risk factors for recurrence of flesh-eating disease?
Risk factors for recurrence include underlying health issues like diabetes, immune suppression, and having open wounds or surgical sites.
How can recurrence of flesh-eating disease be prevented?
Prevention of recurrence involves maintaining good hygiene, proper wound care, managing chronic diseases, and prompt medical attention if symptoms reappear.
What are the symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis?
Symptoms include severe pain, redness, swelling, fever, and the rapid spread of infection. Blisters and skin discoloration may also occur.
What causes flesh-eating disease?
It is primarily caused by bacteria such as group A Streptococcus, but other bacteria can also be involved.
Is it common for flesh-eating disease to recur?
Recurrence is not common; however, any surgical incisions, wounds, or compromised immune systems can increase the risk.
How is necrotizing fasciitis treated?
Treatment involves prompt surgical intervention to remove dead tissue and high doses of intravenous antibiotics.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent recurrence of flesh-eating disease?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and regular medical check-ups, can help reduce the risk of recurrence.
What follow-up care is recommended after treatment of necrotizing fasciitis?
Follow-up care includes monitoring for signs of infection, wound care, and possibly rehabilitation therapy.
Are there any long-term effects after having necrotizing fasciitis?
Long-term effects can include scarring, limb loss, issues with mobility, and psychological impact due to the severity of the disease.
What should someone do if they suspect a recurrence of necrotizing fasciitis?
They should seek immediate medical attention to reduce the risk of serious complications.
Can necrotizing fasciitis spread to other people?
The disease itself generally does not spread from person to person, but the bacteria causing the infection might, especially through direct contact.
What role does the immune system play in the recurrence of necrotizing fasciitis?
An impaired immune system can increase susceptibility to infections and potentially lead to recurrence.
What should be monitored during recovery to detect possible recurrence?
During recovery, it's important to monitor wound sites, look out for new or unusual pain, fever, and redness.
Can ongoing antibiotic treatment prevent recurrence?
Antibiotics are used to treat the infection, but long-term prophylactic antibiotic treatment is typically not recommended unless specified by a healthcare provider.
Do environmental factors contribute to the recurrence of the disease?
Exposure to environments with a high prevalence of streptococcus bacteria and having open wounds could increase the risk.
What kind of surgical intervention is required for necrotizing fasciitis?
Surgical intervention often involves debridement, which is the removal of infected tissue to prevent further spread.
Are there any alternative therapies for preventing recurrence?
Currently, no alternative therapies are proven to prevent recurrence, and traditional medical treatment and prevention methods should be prioritized.
Can stress contribute to the risk of recurrence?
While stress itself doesn't cause infections, chronic stress can weaken the immune system, potentially increasing susceptibility.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 100%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 76%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 73%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 73%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 72%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 67%
-

What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 66%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 66%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 65%
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 65%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 65%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 65%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 64%
-

What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 63%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 62%
-

What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 62%
-

What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 60%
-

Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 58%
-

What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 55%
-

Can testicular cancer recur after treatment?
Relevance: 44%
-

Can Marburg virus disease recur after recovery?
Relevance: 44%
-

Can prostate cancer recur after treatment?
Relevance: 43%
-

Can hypotony recur after treatment?
Relevance: 42%
-

Evidence-Based Interventions: tonsillectomy for recurrent tonsillitis surgery
Relevance: 42%
-

Can BPH recur after treatment?
Relevance: 42%
-
Can postnatal depression recur after treatment?
Relevance: 41%
-

Can Carpal Tunnel Syndrome recur after treatment?
Relevance: 41%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 39%
-

How effective are antibiotics in treating Lyme disease?
Relevance: 37%
-

What treatments are available for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 36%
-

What treatments are available for Alzheimer's disease?
Relevance: 35%
-

What treatments are available for motor neurone disease?
Relevance: 34%
-

Can Lyme disease be treated?
Relevance: 33%
-

Chronic kidney disease: What are the treatments?
Relevance: 32%
-

Can I get impetigo more than once?
Relevance: 30%
-

How does smoking affect Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 30%
-

What role do tumor markers play in testicular cancer?
Relevance: 30%
-

Can you get Lyme disease more than once?
Relevance: 30%
-

Is surgery necessary for Crohn's disease?
Relevance: 29%
-

Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment Offers Hope for Prostate Cancer Patients
Relevance: 28%


